MCS – Age 14 – Cambridge Neuropsychological Test Automated Battery (CANTAB): Cambridge Gambling Task (CGT)
The Millennium Cohort Study (MCS) assessed their cohort members (CMs) during the study’s age 14 sweep using the Cambridge Gambling Task from the Cambridge Neuropsychological Test Automated Battery (CANTAB).
Details on this measure and the data collected from the CMs are outlined in the table below.
| Year of data collection: | 2015 | |||
| Domain: | Executive function (decision making) | |||
| Measures: | The Cambridge Gambling Task was developed to assess decision making and risk-taking behaviour outside a learning context. It can be contrasted with widely used tests including the Balloon Analog Risk Taking Task (BART) and Iowa Gambling Task (IGT) in that the CGT asks participants to make bets under conditions of known risk, rather than ambiguity (e.g., Bechara, Damasio, Tranel & Damasio 2005; Lejuez et al., 2002). The test minimises learning, executive and working memory demands on participants, which can confound the interpretation of test scores. It also separates the decision-making – where participants choose what to bet on – from risk-taking, where participants decide how much then to bet on that choice. | |||
| The test is recommended to assess cognitive function in: Attention deficit disorders, Depression and affective disorders, Obsessive compulsive disorder, Parkinson’s disease, Schizophrenia and Traumatic brain injury. | ||||
| CHC: | Gs (Processing Speed) | |||
| CLOSER source: | Explore this sweep in Discovery: MCS Age 14 Survey (2015) | |||
| Gt (Decision Speed/Reaction Time) | ||||
| Administrative method: | Self-completion on Computer-Assisted Personal Interview (CAPI) tablet; using the CANTAB eclipse software which was integrated into the CAPI interview. | |||
| Procedure: | The participant was presented with a row of ten boxes across the top of the screen: some were red and some are blue. The ratio of red and blue boxes varied between stages but there was always one box that contained a yellow token. Participants used the ‘Red’ and ‘Blue’ buttons at the bottom of the screen to choose the box colour in which they thought the token was hidden. | |||
| In the assessed stages, participants started with 100 points and selected a proportion of these points to bet on their decision. A circle in the centre of the screen displayed the current bet value, which would either incrementally increase or decrease (depending on the task variant selected). Participants pressed this button when it showed the proportion of their score they would like to bet. These points were either added or taken away to their total score, depending on their decision and where the token was actually hidden. | ||||
| Duration: max 18 minutes | ||||
| Link to questionnaire: | Documentation not available. | |||
| For some additional detail, see: Cambridge Cognition web page on Cambridge Gambling Task (opens in new tab) | ||||
| Scoring: | Raw data and procedures / algorithms for deriving the summary scores are unavailable. There are currently no normative scores. | |||
| Item-level variable(s): | Not readily available | |||
| FCGTOUTCM (outcome of test) | ||||
| Other item-level variables not readily available. | ||||
| There are also no additional variables available outlining any technical problems. | ||||
| Test condition variables are contained in data file “mcs6_cm_assessment” from UK Data Service. | ||||
| Total score/derived variable(s): | FCGTTTIME (Test duration) | |||
| FCGTDELAY (Delay aversion) | ||||
| FCGTDTIME (Deliberation time – milliseconds) | ||||
| FCGTOPBET (Overall proportional bet) | ||||
| FCGTQOFDM (Quality of decision making) | ||||
| FCGTRISKA (Risk adjustment) | ||||
| FCGTRISKT (Risk taking) | ||||
| Age of participant (months): | Mean = 171, SD = 4.05, Range = 158 – 184 | |||
| Descriptives: | FCGTDTIME | FCGTDELAY | FCGTOPBET | |
| (deliberation time) | (Delay aversion) | (Overall proportional bet) | ||
| N | 10,854 | 10,848 | 10,848 | |
| Range | 362 – 23691 | -0.9 – 0.9 | 0.05 – 0.95 | |
| Mean | 2336.53 | 0.27 | 0.48 | |
| SD | 944.16 | 0.22 | 0.14 | |
(click image to enlarge) |
(click image to enlarge) |
(click image to enlarge)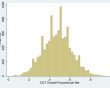 |
||
| FCGTQOFDM (Quality of decision making) | FCGTRISKA (Risk adjustment) | FCGTRISKT (Risk taking) | ||
| N | 10,854 | 10,853 | 10,853 | |
| Range | 0 – 1 | -4.06 – 5.28 | 0.05 – 0.95 | |
| Mean | 0.88 | 0.99 | 0.52 | |
| SD | 0.13 | 0.98 | 0.15 | |
(click image to enlarge) |
(click image to enlarge)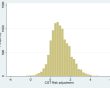 |
(click image to enlarge) |
||
| Other sweep and/or cohort: | MCS – Age 11 – CANTAB Gambling Task | |||
| Source: | Cambridge Cognition. CANTAB (Cambridge Neuropsychological Test Automated Battery) – Cognitive Assessment Software. Available at: Cambridge Cognition web page on cognitive function (opens in new tab) | |||
| Technical resources: | Atkinson, M. (2015). Millennium Cohort Study Interpreting the CANTAB Cognitive Measures. (opens in new tab) London, UK: Centre for Longitudinal Studies, Institute of Education, University of London. | |||
| Ipsos MORI. (2017). Millennium Cohort Study Sixth Sweep (MCS6) Technical Report (Version 2). (opens in new tab) London, UK: Ipsos MORI Social Research Institute. | ||||
| Fitzsimons, E. (2020). Millennium Cohort Study Sixth Survey 2015-2016 User Guide (Second Edition). (opens in new tab) London UK: Centre for Longitudinal Studies, University College London. | ||||
| Example articles: | Creese, H., Viner, R., Hope, S., & Christie, D. (2018). Obesity and cognition during childhood: Findings from the Millennium Cohort Study: Hanna Creese. European Journal of Public Health, 28(suppl_4), cky213-260. | |||
