The MRC National Survey of Health of Development (NSHD) assessed their cohort members (CMs) during the study’s age 60-64 sweep using the Verbal Learning/Word List Recall Test.
Details on this measure and the data collected from the CMs are outlined in the table below.
| Years of data collection: | 2006-2010 |
| Domain: | Verbal (memory) |
| Measures: | Attention |
| Short-term episodic memory | |
| Verbal memory | |
| Free-recall memory | |
| CHC: | Glr (Long-Term Storage and Retrieval) |
| CLOSER Source: | Explore this sweep in CLOSER Discovery: NSHD 2006-2010 (Age 60-64) (opens in a new tab) |
| Administration method: | Research nurse; face to face; pen and paper |
| Procedure: | Same procedure as NSHD Age 53 |
| Link to questionnaire: | https://skylark.ucl.ac.uk/NSHD/lib/exe/fetch.php?media=questionnaires:2008_nurse.pdf (opens in new tab) |
| Scoring: | A point was awarded for every correct word recalled (0 - 45 [immediate]; 0 - 15[delayed]) |
| Item-level variable(s): | WLE109 - WLTD09 |
| Total score/derived variable(s): | WLT09 |
| Descriptives: | Raw score |
| N = 2,150 | |
| Range = 4 - 43 | |
| Mean = 24.26 | |
| SD = 6.11 | |
(click image to enlarge)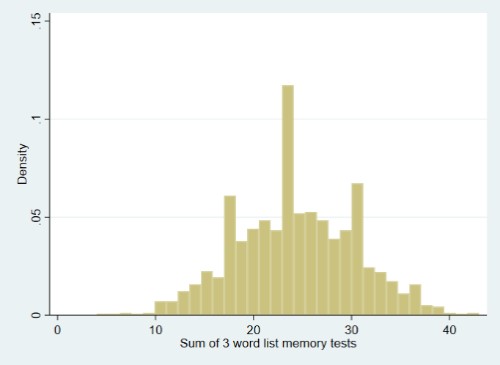 |
|
| Age of participants (months): | Mean = 760.24, SD = 13.36, Range = 724 - 780 |
| Other sweep and/or cohort: | NCDS – Age 50 – Verbal Learning/Word List Recall Test (Immediate and Delayed) (1 trial only; 10 words, presented aurally) |
| NCDS – Age 62 – Proposed repeat of tests at age 50 | |
| BCS70 – Age 46-47 – Verbal Learning/Word List Recall Test (Immediate and Delayed) (1 trial only; 10 words, presented aurally) | |
| NSHD – Age 43 – Verbal Learning/Word List Recall Test | |
| NSHD – Age 53 – Verbal Learning/Word List Recall Test | |
| NSHD – Age 68-70 – Verbal Learning/Word List Recall Test | |
| Source: | This task was developed specifically for this study by the NSHD team led by Prof Bryan Rodgers. Similar tasks have been used to measure verbal learning for decades, e.g. Bush and Mosteller (1955). |
| Technical resources: | None |
| Example articles: | Hurst, L., Stafford, M., Cooper, R., Hardy, R., Richards, M., & Kuh, D. (2013). Lifetime socioeconomic inequalities in physical and cognitive aging. American Journal of Public Health, 103(9), 1641-1648. |
| James, S. N., Davis, D., O'Hare, C., Sharma, N., John, A., Gaysina, D., ... & Richards, M. (2018). Lifetime affective problems and later-life cognitive state: Over 50 years of follow-up in a British birth cohort study. Journal of Affective Disorders, 241, 348-355. |
Go to:
- Overview of all cognitive measures in NSHD
- Overview of adulthood cognitive measures across all studies
This page is part of CLOSER’s ‘A guide to the cognitive measures in five British birth cohort studies’.
