The 1958 National Child Development Study (NCDS) assessed their cohort members (CMs) during the study’s age 11 sweep using the Mathematics Test.
Details on this measure (devised by the National Foundation for Educational Research) and the data collected from the CMs are outlined in the table below.
| Year of data collection: | 1969 |
| Domain: | Arithmetic |
| Measures: | Arithmetic |
| CHC: | Gq (Quantitative Knowledge) |
| CLOSER Source: | Explore this sweep in CLOSER Discovery: NCDS Age 11 Survey 1969 (opens in a new tab) |
| Administrative method: | Teacher at school; individually face to face; pen and paper |
| Procedure: | The test consisted of 40 items. The test included, number skills, fractions, measures and geometry. Most questions were calculated directly, with a few involving multiple-choice answers. |
| Link to questionnaire: | https://cls.ucl.ac.uk/wp-content/uploads/2017/07/NCDS2-Guide-to-the-Dataset.pdf (opens in new tab) |
| Scoring: | One mark was awarded for each correct answer |
| Item-level variable(s): | Not currently available |
| Total score/derived variable(s): | n926 |
| Age of participant (months): | Mean = 134.25, SD = 1.70, Range = 130 - 152 |
| Descriptives: | Raw score |
| N = 14,126 | |
| Range = 0 - 40 | |
| Mean = 16.63 | |
| SD = 10.35 | |
(click image to enlarge)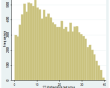 |
|
| Other sweep and/or cohort: | None |
| Source: | Constructed by National Foundation for Educational Research (NFER) specifically for use in the NCDS |
| Technical resources: | Shepherd, P., Measures of ability at ages 7 to 16. National Child Development Study User Guide, 2012. |
| Example articles: | Cherlin, A. J., Furstenberg, F. F., Chase-Lansdale, L., Kiernan, K. E., Robins, P. K., Morrison, D. R., & Teitler, J. O. (1991). Longitudinal studies of effects of divorce on children in Great Britain and the United States. Science, 252(5011), 1386-1389. |
| Gregg, P., & Macmillan, L. (2010). Family income, education and cognitive ability in the next generation: exploring income gradients in education and test scores for current cohorts of youth. Longitudinal and Life Course Studies, 1(3), 259-280. |
Go to:
- Overview of all cognitive measures in NCDS
- Overview of childhood cognitive measures across all studies
This page is part of CLOSER’s ‘A guide to the cognitive measures in five British birth cohort studies’.
