The Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC) assessed their cohort members (CMs) during the study’s age 8.5 sweep (Focus@8) using the Sky Search measure of selective attention and motor control from the Test of Everyday Attention for Children (TEA-Ch).
Details on this measure and the data collected from the CMs are outlined in the table below.
| Years of data collection: | 1999-2001 | ||
| Domain: | Attention | ||
| Measures: | Selective attention | ||
| Concentration | |||
| Mental speed | |||
| Visual scanning | |||
| CHC: | Gs (Processing Speed) | ||
| Gps (Psychomotor Speed) | |||
| Gv (Visual Processing) | |||
| Gsm (Short-Term Memory) | |||
| CLOSER Source: | Explore this sweep in CLOSER Discovery: ALSPAC Childhood (5 years to 12 years 11 months) (opens in a new tab) | ||
| Administration method: | Trained interviewer; clinical setting; pen and paper | ||
| Procedure: | The child was presented with an array of non-identical and identical spaceships, and was tasked with circling pairs of identical spaceships as quickly as possible, whilst trying to avoid any errors. The interviewer provided a demonstration, and the child worked through a practice sheet before commencing the test. After the practice sheet, the child was presented with a larger sheet and asked to do the same (20 identical pairs). The above task was then repeated, without the non-identical pairs of ships. The aim was to identify how quickly the child could complete the task, in order to control for motor performance. | ||
| Link to questionnaire: | http://www.bristol.ac.uk/alspac/researchers/our-data/clinical-measures/ (opens in new tab) | ||
| Scoring: | Three summary scores are provided: | ||
| i. unadjusted score: time taken (in seconds) for the search task divided by the number of spaceship pairs correctly circled | |||
| ii. motor score: time in seconds for the motor task divided by number of correct pairs | |||
| iii. The adjusted score is calculated by subtracting the motor score from the unadjusted score, thus controlling for motor speed | |||
| iv. A normative score is also available, however the ALSPAC codebook recommends this is used with caution, as the original sample used to create the normative scores was small (N = ~100) | |||
| Item-level variable(s): | f8at003-f8at061 | ||
| Total score/derived variable(s): | f8at061, f8at062, f8at065 Explore these variables in CLOSER Discovery: ALSPAC Focus at 8 Clinic Dataset (opens in a new tab) |
||
| Descriptives: | Unadjusted score | Motor score | Adjusted score |
| N = 7,249 | N = 7,219 | N = 7,184 | |
| Range = 1.94 - 48.33 | Range = 0.35 - 7 | Range = -4.05 - 46.58 | |
| Mean = 6.58 | Mean = 1.37 | Mean = 5.20 | |
| SD = 2.07 | SD = 0.46 | SD = 1.92 | |
(click image to enlarge)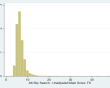 | (click image to enlarge) | (click image to enlarge)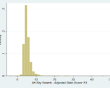 |
|
| Age of participants (months): | Mean = 103.82 months, SD = 3.92, Range = 89 - 127 | ||
| Other sweep and/or cohort: | ALSPAC – Age 11.5 – TEA-Ch Sky Search | ||
| Source: | Robertson, I. H., Ward, T., Ridgeway, V., & Nimmo-Smith, I. (1996). The structure of normal human attention: The Test of Everyday Attention. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 2(6), 525-534. | ||
| Manly, T., Anderson, V., Nimmo-Smith, I., Turner, A., Watson, P., & Robertson, I. H. (2001). The differential assessment of children's attention: The Test of Everyday Attention for Children (TEA-Ch), normative sample and ADHD performance. The Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 42(8), 1065-1081. | |||
| Technical resources: | Heaton, S. C., Reader, S. K., Preston, A. S., Fennell, E. B., Puyana, O. E., Gill, N., & Johnson, J. H. (2001). The Test of Everyday Attention for Children (TEA-Ch): Patterns of performance in children with ADHD and clinical controls. Child Neuropsychology, 7(4), 251-264. (Link opens in a new tab) | ||
| Example articles: | Chandramouli, L., Steer, C. D., Ellis, M., & Emond, A. M. (2009). Effects of early childhood lead exposure on academic performance and behaviour of school age children. Archives of Disease in Childhood, 94(11), 844-8. | ||
| Odd, D. E., Emond, A., & Whitelaw, A. (2012). Long-term cognitive outcomes of infants born moderately and late preterm. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology, 54(8), 704-709. | |||
For the named items in the table above, links are provided to their corresponding content on CLOSER Discovery. Where a variable range is provided, full variable lists can be accessed through the ‘Variable Groups’ tab on the linked Discovery page.
Go to:
- Overview of all cognitive measures in ALSPAC
- Overview of childhood cognitive measures across all studies
This page is part of CLOSER’s ‘A guide to the cognitive measures in five British birth cohort studies’.
