The Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC) assessed their cohort members (CMs) at 49 months’ age (Children in Focus Clinic) using the Arithmetic measure from the Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence Revised (WPPSI-RUK).
Details on this measure and the data collected from the CMs are outlined in the table below.
| Year of data collection: | 1996-1997 |
| Domain: | Arithmetic ability |
| Measures: | Numeric reasoning |
| Sequential processing | |
| CHC: | Gq (Quantitative Knowledge) |
| CLOSER Source: | Explore this sweep in CLOSER Discovery: ALSPAC Early Years (13 months to 4 years 11 months) (opens in a new tab) |
| Administration method: | Trained interviewer; clinical setting; pointing; questions and answers delivered orally |
| Procedure: | The test contained 23 items. For items 1-7, the child was asked to point to an object that illustrated a particular quantitative characteristic on a visually presented array of objects. For items 8-11 the child demonstrated numeric knowledge by counting and manipulating blocks. For items 12-23, the child solved arithmetic problems that were read aloud by the interviewer. There was a time-limit for each of questions 12-23. If the child held up the correct number of fingers to indicate a numeric response, this was accepted. |
| Link to questionnaire: | http://www.bristol.ac.uk/alspac/researchers/our-data/clinical-measures/ (opens in new tab) |
| Scoring: | Standardised score (M = 10, SD = 3) |
| Item-level variable(s): | Not readily available |
| Total score/derived variable(s): | cf808 Explore this variable in CLOSER Discovery: ALSPAC Children in Focus 4Mth-61Mth Clinics Dataset (opens in a new tab) |
| Descriptives: | Raw score |
| N = 1,015 | |
| Range = 1 - 19 | |
| Mean = 10.02 | |
| SD = 2.56 | |
(click image to enlarge)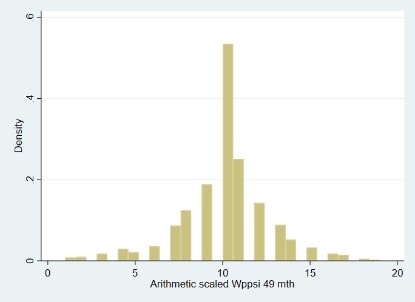 |
|
| Age of participants: | Mean = 212.39 weeks, SD = 1.63, Range = 207-221 |
| Other sweep and/or cohort: | None |
| Source: | Wechsler, D. (1989). Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence-Revised. WPPSI-R. Psychological Corporation. |
| Technical resources: | Kaufman, A. S., & Lichtenberger, E. O. (2000). Essentials of WISC-III and WPPSI-R Assessment. John Wiley & Sons Inc. |
| Example articles: | Gathercole, S. E., Briscoe, J., Thorn, A., Tiffany, C., & ALSPAC Study Team. (2008). Deficits in verbal long-term memory and learning in children with poor phonological short-term memory skills. The Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology, 61(3), 474-490. |
| Taylor, C. M., Kordas, K., Golding, J., & Emond, A. M. (2017). Data relating to prenatal lead exposure and child IQ at 4 and 8 years old in the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children. Neurotoxicology, 62, 224-230. |
For the named item in the table above, a link is provided to the corresponding CLOSER Discovery content.
Go to:
- Overview of all cognitive measures in ALSPAC
- Overview of childhood cognitive measures across all studies
This page is part of CLOSER’s ‘A guide to the cognitive measures in five British birth cohort studies’.
