The Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC) assessed their cohort members (CMs) during the study’s age 15.5 sweep (TeenFocus 3) using the Inhibition (Stop Signal Task) measure.
Details on this measure and the data collected from the CMs are outlined in the table below.
| Years of data collection: | 2006-2008 | |
| Domain: | Reaction time | |
| Measures: | Choice reaction time | |
| Response inhibition | ||
| CHC: | Gt (Decision Speed/Reaction Time) | |
| CLOSER Source: | Explore this sweep in CLOSER Discovery: ALSPAC Adolescence (13 years – 18 years 11 months) (opens in a new tab) | |
| Administration method: | Trained interviewer; clinical setting; computer-assisted personal interview (CAPI) | |
| Procedure: | Sitting in front of the computer monitor, the child was instructed to place their two index fingers in two stimulus boxes, labelled X and O respectively. Two types of trials were performed: primary task trials and stop signal trials. For the primary task, the child was asked to focus on a small smiley face presented in the centre of the computer screen. An X or O would then be presented on the screen and the child had to press the corresponding button as fast as possible. A mean reaction time was calculated (this is used to calculate a tone delay used in subsequent trials; see below). The stop signal task was identical to the primary task except that a bleep (stop signal) was heard randomly after the X or O appears (the go signal). If the bleep was not heard the child was asked to press the corresponding button according to what was presented on screen. When the bleep was sounded the child was told to refrain from pressing the response button, therefore inhibiting the stimulus response. The bleep sounded on random trials at 150 ms or 250 ms before the child's reaction time (as calculated in the Primary Task Trials). For those children that were deaf or had severe hearing difficulties, a visual stop signal was used instead. For those children who could only use one hand, a one-handed stimulus box was used. The young person receives four blocks of trials. The first block consisted of Xs and Os with no beeps (30 trials in total) - the young person practiced the button presses here. The second block consisted of Xs, Os and beeps (24 trials in total 8 of which have a beep) - the young person practiced the button presses with beeps here. The third and fourth blocks were the actual experimental trials. Each experimental block consisted of 48 trials total in each. 32 of those trials were without beeps, and 16 trials were with beeps. | |
| Link to questionnaire: | http://www.bristol.ac.uk/alspac/researchers/our-data/clinical-measures/ (opens in new tab) | |
| Scoring: | Mean reaction time across different conditions. | |
| Item-level variable(s): | Not readily available | |
| Total score/derived variable(s): | fh6910 – fh6953 Explore these variables in CLOSER Discovery: ALSPAC Teen Focus 3 Clinic Dataset (opens in a new tab) |
|
| Descriptives: | Correct block 1 (mean RT) | Correct type p (mean RT) |
| N = 5,252 | N = 5,252 | |
| Range = 45 - 841 | Range = 284 - 831 | |
| Mean = 423.78 | Mean = 568.78 | |
| SD = 66.95 | SD = 81.40 | |
(click image to enlarge)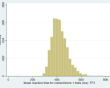 | (click image to enlarge)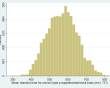 |
|
| Incorrect type s (mean RT) | Incorrect type ss (mean RT) | |
| N = 2,734 | N = 4,344 | |
| Range = 49 - 999 | Range = 1 - 995 | |
| Mean = 448.55 | Mean = 464.52 | |
| SD = 139.25 | SD = 87.95 | |
(click image to enlarge)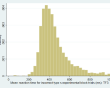 | (click image to enlarge)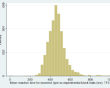 |
|
| Age of participants (months): | Mean = 185.69 months, SD = 4.24, Range = 171 - 212 | |
| Other sweep and/or cohort: | ALSPAC – Age 10 – Inhibition (Stop-Signal Task) | |
| Source: | Logan, G. D., Cowan, W. B., & Davis, K. A. (1984). On the ability to inhibit simple and choice reaction time responses: a model and a method. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 10(2), 276. | |
| Technical resources: | None | |
| Example articles: | Pindus, D. M., Davis, R. D. M., Hillman, C. H., Bandelow, S., Hogervorst, E., Biddle, S. J., & Sherar, L. B. (2015). The relationship of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity to cognitive processing in adolescents: findings from the ALSPAC birth cohort. Psychological Research, 79(5), 715-728. | |
| Wallace, S., & Linscott, R. J. (2018). Intra-individual variability and psychotic-like experiences in adolescents: Findings from the ALSPAC cohort. Schizophrenia Research, 195, 154-159. | ||
For the named items in the table above, links are provided to their corresponding content on CLOSER Discovery. Where a variable range is provided, full variable lists can be accessed through the ‘Variable Groups’ tab on the linked Discovery page.
Go to:
- Overview of all cognitive measures in ALSPAC
- Overview of childhood cognitive measures across all studies
This page is part of CLOSER’s ‘A guide to the cognitive measures in five British birth cohort studies’.
